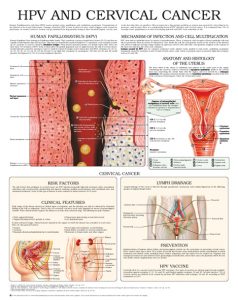
Human Papillomavirus Infection (HPV) and Cervical Cancer
Human Papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes genital warts, papillomas and condyloma acuminata. Transmission of the disease is by sexual intercourse. Damage caused by HPV is easy to detect in men, which triggers early consult to physicians. In women, however, lesions can go unnoticed for long periods owing to their location (vagina, cervix), and to the fact that they are painless. This accounts for a big sanitary problem as women may spread the virus blind to its presence, and because there is a relationship between HPV infection and cervical cancer. It is estimated that 70% of sexually-active population is at risk of becoming infected with HPV virus sometime in life.
[hfe_template id=’14716′]
[hfe_template id=’16373′]