Anatomy of the Ear
aAsthma & COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (II)
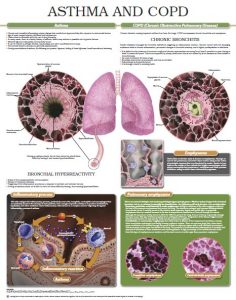
Asthma
• Chronic and reversible inflammatory airway disease that results from hyperreactivity after exposure to various risk factors.
• Age of onset ranges between childhood and adolescence.
• Obstruction is reversible with the use of drug theraphy.
• In many cases, there is a family history of asthma, which may indicate a possible role of genetic factors.
• Elevated IgE and eosinophilia is frequently found.
• It can be related to allergic rhinitis, nasal polyps and other manifestations of atopy.
• The periods between attacks are generally asymptomatic.
• During exacerbations of asthma, the following are present: dyspnea, feeling of chest tightness, breath sounds and wheezing.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Smoke inhalation damages the bronchial epithelium triggering an inflammatory reaction. Chronic contact with the damaging substance leads to chronic inflammation, permanent changes in bronchial anatomy, and a higher predisposition to infections.
• It is defined as the presence of recurrent cough and chronic expectoration occurring for at least 3 months in a year during at least 2 consecutive years. This is accompanied by airway obstruction that is not caused by such diseases as tuberculosis or bronchiectasis.
• Its onset is between 45 years of age.
• Bronchial obstruction is permanent and thus irreversible.
• Polycythemia is frequently found.
• It is strongly related to smoking habit.
[hfe_template id=’14716′]
[hfe_template id=’16832′]